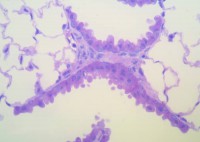
Over the past 20 years, the rate of cancer death in the U.S. has dropped a gratifying 20%, with the exception of thyroid cancer. Bucking the general trend, thyroid cancer deaths have increased slightly over the last two decades with the number of new thyroid cancer diagnoses climbing steadily, particularly among women.
Thyroid cancer accounts for only 3.6% of all new cancer diagnoses in the U.S. and just 0.3% of cancer deaths, according to the National Cancer Institute. Considered a highly treatable form of cancer, thyroid cancer has a 97.7% five-year survival rate. Even so, that thyroid cancer cases have doubled during a period when other cancer diagnoses have declined has researchers puzzled – and concerned. While better diagnostic tools and early detection certainly account for a portion of the increase, many cancer researchers believe that something else may be behind thyroid cancer’s increasing incidence and mortality. As the New York Times explained, of particular concern is the fact that thyroid cancer mortality among men, who are 3 times less likely than women to develop the disease, increased an alarming 2.4% between 1992 and 2000, the greatest increase of any type of cancer.
An additional issue is overtreatment of so called “small tumors,” tiny thyroid tumors that are unlikely to cause a problem during the patient’s lifetime. Questioning the need for surgical removal, the typical treatment for thyroid tumors, in such cases, Dr. Bryan McIver of the Mayo Clinic told the Times, “Even though the evidence does not support that it is beneficial, there is an increasing trend in the U.S., and probably worldwide, to treat all thyroid cancers in the most aggressive way.”
Integrated immunotherapy offers thyroid cancer patients a non-toxic treatment option that may be particularly effective in the treatment of small tumors.