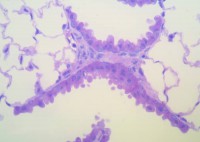
Researchers in Spain have discovered an unexpected similarity between the behaviors of cancer cells and the cells that form human embryos that could some day lead to new cancer treatments to prevent cancer from metastasizing. (Visit this link to read the original article by M. Angela Nieto of the Instituto de Neurociencias Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas published in Science magazine.)
When human embryos form, embryonic cells must migrate from the initial cellular core to new locations where they form different types of tissues and organs. When they are tasked to become heart cells or skin cells or bone cells, embryonic cells must undergo two complex genetic transformations that require remarkable cell plasticity.
In processes that involve gene splicing and micro-RNA networking, embryonic cells undergo a transformation that allows them to become mobile and move to specific designated locations in the developing body. Scientists call this process epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, or EMT. Once embryonic cells have arrived at their designated location, they undergo a second transformation that restores their ability to replicate and allows them to assume their newly assigned differentiated form heart cells or skin cells or bone cells, etc. Scientists call this “reverse” process mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition, or MET.
Spanish researchers have observed this same two-step process – EMT followed by MET — when cancer cells metastasize. EMT occurs when cancer cells leave their primary tumor and travel to other parts of the body. When they arrive at new locations, MET occurs, allowing cancer cells to replicate and form secondary tumors. Other research indicates that changes in the tumor microenvironment may initiate these processes in cancer tumors.